Shiba Inu (details)
Maybe many people don't know that dogs, like humans, also suffer from anemia. So what are the causes of anemia in dogs, what symptoms will appear, and how should we prevent dogs from developing anemia?
I. What is anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the red blood cell count (RBC) and hemoglobin content (MCHC) per unit volume of blood in a dog are lower than normal.
2. Causes, symptoms and prevention of anemia
There are many reasons for anemia in dogs. In addition to the common malnutrition and anemia caused by massive bleeding, many diseases will show symptoms of anemia, which makes the diagnosis quite complicated (see Figure 1 and Figure 2). Therefore,
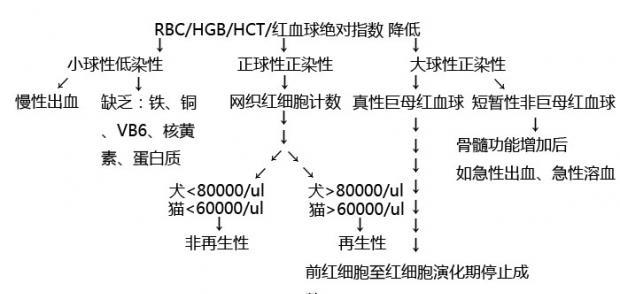
Figure 1: Anemia Diagnosis 1
Figure 2: Anemia Diagnosis 2
1. Hemorrhagic anemia
1.1 Acute hemorrhagic anemia
Reason: It is generally caused by a large amount of blood loss in the dog's body in a short period of time due to external force (surgery or trauma).
Symptoms: massive bleeding; pale skin and mucous membranes (see Figure 3); collapse; muscle tremors; decreased blood pressure; shock, etc.
Figure 3: Pale mucous membranes in dogs
Prevention: Be sure to tie the dog leash when you go out to walk the dog, and the dog leash should not be too long to avoid accidents.
Emergency treatment: The owner should take the dog to see a doctor as soon as possible. If a large wound is visible, the owner can immediately seek medical attention after tying the dog's wound with a rope or rubber band.
1.2 Chronic hemorrhagic anemia
Reasons: It is generally caused by chronic hemorrhagic inflammation in the internal organs of dogs; canine hemophilia; canine hookworm; a large number of ticks and lice (see Figure 4).
Figure 4: Ticks bite most in the ear canal
Symptoms: The dog is thin; the skin and mucous membranes gradually become white; lethargy; lethargy; fast and weak heartbeat; edema of the lower jaw and limbs; shock, etc.
prevention:
1. Chronic hemorrhagic inflammation of viscera: Pay attention to the usual scientific feeding, and avoid feeding spoiled, rotten, frozen or food containing a large number of animal lymph nodes, and also avoid feeding too much at one time after being hungry.
2 Canine hemophilia: This disease is a hemorrhagic diathesis caused by a recessive hereditary blood coagulation disorder.
3 Canine hookworm disease and a large number of ticks and lice parasites: Regular deworming, prohibition of scattering, and do not allow dogs to move freely in the wild (especially in the forest and grass).
2. Hemolytic anemia
Causes: Mainly due to the massive destruction of red blood cells caused by infectious diseases (Babesia, hemolytic streptococcus infection, etc.), poisoning (lead, copper, benzene, phenol, etc.), antigen-antibody reactions, and other such as myeloid leukemia.
Symptoms: visible mucous membrane yellow staining; listlessness; weight loss; lethargy; hemoglobinuria, etc.
Prevention: regular deworming; regular immunization; pay attention to walking the dog, do not let it swallow the food on the road, and do not let it drink water in rivers, lakes, ponds; do not let it come into contact with toxic and harmful substances; do not go to the lack of qualifications
Hemolytic anemia in newborn puppies is caused by the difference in blood type matching between puppies and mother dogs.
Figure 5: Dog undergoing blood transfusion
3. Nutritional anemia
Reason: It is mainly caused by the lack of hematopoietic substances such as protein, trace elements and vitamins, which affects the normal production of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
Symptoms: The dog is thin; the coat is rough; malnutrition; pale skin and mucous membranes; lethargy; weakness of the limbs, etc.
Prevention: The lack of the above hematopoietic substances is mainly caused by the disturbance of the intestinal absorption function of dogs caused by single food, chronic digestive tract diseases and intestinal parasites.
4. Aplastic anemia
Reason: Mainly due to bone marrow hematopoietic dysfunction caused by poisoning, radiation damage, chronic kidney disease and other diseases.
Symptoms: the dog is thin; shortness of breath; pale skin and mucous membranes; lethargy; weakness of the limbs, etc.
Prevention: Pay attention to scientific feeding, try not to feed human food (such as chocolate, high-salt food, etc.); do not expose dogs to radioactive elements unless necessary (X-ray examination, etc.).
