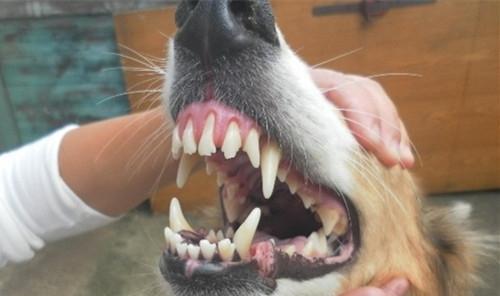
Scottish Shepherd Dog (detail introduction)
If the dog's dental disease is very serious, it is very painful to know that it is very painful for the dog. Periodontal diseases of dogs are also slowly developing. The gums are atrophy from plaque to dental stones. Hurry up and see what your dog's teeth do not like to brush your teeth now.
I. Stylee plaque
There are many bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria are attached to the surface of the teeth by saliva. After continuous breeding, about 2-3 days will grow into a obvious layer of yellow and white "dirt". This is the plaque. The plaque can cause the gums of immune response, and the gums will become red (congested), swelling (blunt edges), that is, slight gingivitis. Plasma plaque and gingivitis are the first step to cause periodontal disease.
Two, dental stones
Mild gingivitis does not necessarily become periodontal disease. Because the plaque can be easily removed by brushing, the friction when eating is also removed. The plaque disappears, and the gums are restored. However, if the plaque has not been removed. After about a few days, these bacteria died one after another, and the "corpse" of the bacteria will slowly calcify, and it becomes gray -yellow dental stones. The dental stones will become thicker layer by layer, which will cause the gums to be more serious. Then below the crown will be violated. The connective tissue of the teeth will be destroyed.
Three, gum retract
If gingivitis and dental stones are continuously stimulated, it will evolve into periodontitis. In addition to the meat that affects the gums and the connective tissue around the gums, it can also cause destruction of alginic bone. Once the bone bone is destroyed, the entire gums will shrink, revealing the roots without enamel protection. At the same time, the teeth will start to shake, forming severe periodontal disease. And the periodontal disease is not just letting the baby drop the teeth. The inflammation of the gums can cause wounds, ulcers, and bacterial infections; the destruction of the alginic bone can make the upper and lower jaw bones fragile; The nasal cavity and compression of the eyes; the discomfort of the oral cavity makes the baby unwilling to eat, and so on.
